In Section we will learn how to use the PostgreSQL MAKE_INTERVAL() function. The make_interval() Function in PostgreSQL is used to create an interval by taking the arguments as input. This function allows you to specify intervals in terms of years, months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds and it constructs an interval accordingly.
Syntax for make_interval() Function in PostgreSQL:
MAKE_INTERVAL(time interval => value, time interval => value,..)
Parameters:
- years: Number of years in the interval.
- months: Number of months in the interval.
- weeks: Number of weeks in the interval.
- days: Number of days in the interval.
- hours: Number of hours in the interval.
- mins: Number of minutes in the interval.
- secs: Number of seconds in the interval.
Note: All parameters are optional, and the default value for each is 0 if not specified.
Creating interval using MAKE_INTERVAL() function:
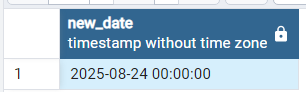
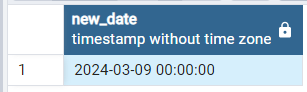
Creating interval of 1 year 6 months to date using MAKE_INTERVAL() function :
In the below Example we will be passing “years” & “months” as time interval argument and 1 & 6 as unit argument in order to add 1 year 6 months to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(years=> 1,months=>6) as new_date
Output:
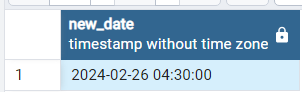
Creating interval 2 days, 4 hours, and 30 minutes:
In the below Example we will be passing “days”, ”hours” & “minutes” as time interval argument and 1 & 6 as unit argument in order to add 1 year 6 months to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(days=>2,hours=>4,mins=>30) as new_date
Output:
PostgreSQL MAKE_INTERVAL() function example
Below are some of the Examples for MAKE_INTERVAL() function in postgresql.
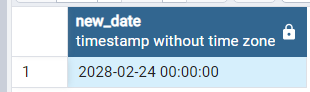
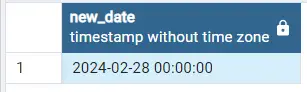
- Add years to date using MAKE_INTERVAL() function in postgresql:
In the below Example we will be passing “years” as time interval argument and 4 as unit argument in order to add 4 years to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(years=>4) as new_date
Output:
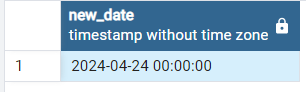
- Add months to date using MAKE_INTERVAL() function in postgresql:
In the below Example we will be passing “months” as time interval argument and 2 as unit argument in order to add 2 months to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(months=>2) as new_date
Output:
- Add weeks to date using MAKE_INTERVAL() function :
In the below Example we will be passing “weeks” as time interval argument and 2 as unit argument in order to add 2 weeks to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(weeks=>2) as new_date
Output:
- Add days to date using MAKE_INTERVAL() function :
In the below Example we will be passing “days” as time interval argument and 4 as unit argument in order to add 4 days to date.
SELECT '2024-02-24'::date + make_interval(days=>4) as new_date
Output:
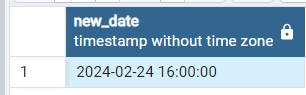
- Add hours to datetime using MAKE_INTERVAL() function :
In the below Example we will be passing “hours” as time interval argument and 4 as unit argument in order to add 4 hours to datetime.
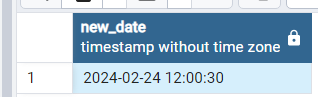
SELECT ' 2024-02-24 12:00:00'::timestamp + make_interval(hours=>4) as new_date
Output:
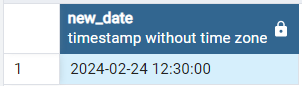
- Add minutes to datetime using MAKE_INTERVAL() function:
In the below Example we will be passing “mins” as time interval argument and 30 as unit argument in order to add 30 minutes to datetime.
SELECT ' 2024-02-24 12:00:00'::timestamp + make_interval(mins=>30) as new_date
Output:
- Add seconds to datetime using MAKE_INTERVAL() function in postgresql:
In the below Example we will be passing “secs” as time interval argument and 30 as unit argument in order to add 30 seconds to datetime.
SELECT ' 2024-02-24 12:00:00'::timestamp + make_interval(secs=>30) as new_date
Output:
MAKE_INTERVAL() function in PostgreSQL Example 1
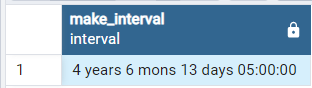
The following example uses the MAKE_INTERVAL() function to create an interval that represents 4 year, 6 months, 13 days, and 5 hours:
SELECT MAKE_INTERVAL(years => 4, months => 6, days => 13, hours => 5);
Output:
MAKE_INTERVAL() function in PostgreSQL Example 2
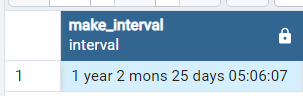
The following example uses the MAKE_INTERVAL() function to create an interval that represents year, months, days, hours, minutes and seconds. In the below Example 3rd and 4th Argument combined to create days i.e. 3 weeks (21 days) + 4 days = 25 days
SELECT MAKE_INTERVAL(1,2,3,4,5,6,7);
Output:
MAKE_INTERVAL() function in Postgres Example 2
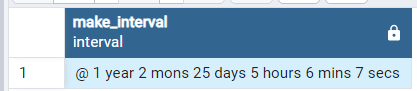
The following example uses the MAKE_INTERVAL() function to create an interval that represents year, months, days, hours, minutes and seconds and output them verbally.
SET intervalstyle = 'postgres_verbose'; SELECT make_interval(1,2,3,4,5,6,7);
Output: