In order to calculate Log values in SAS we will be using LOG Function. LOG Function in SAS consist of LOG, LOG2, LOG10 Function. LOG2 Function in SAS. LOG10 Function in SAS. Let’s see an example of each.
- LOG Function in SAS – Log of the column in SAS.
- LOG10 Function in SAS – Log10 of the column in SAS.
- LOG2 Function in SAS – Log2 of the column in SAS.
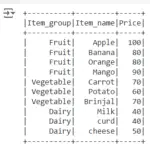
So we will be using EMP_DET Table in our example

LOG function in SAS – SYNTAX
The following statements illustrate the LOG function:

LOG Function in SAS – LOG()
LOG() Function in SAS takes column as argument and converts column to logarithmic value
data EMP_DET1; set EMP_DET; LOG_salary = LOG(salary_in_USD); run;
So the resultant table with logarithmic value will be

LOG2 function – Syntax
The following statements illustrate the LOG2 function:

LOG2 Function in SAS – LOG2()
LOG2() Function in SAS takes column as argument and converts column to log value to the base 2.
data EMP_DET1; set EMP_DET; LOG2_salary = LOG2(salary_in_USD); run;
So the resultant table with logarithmic base 2 value will be

LOG10 function – Syntax
The following statements illustrate the LOG10 function:
LOG10 Function in SAS – LOG10()
LOG10() Function in SAS takes column as argument and converts column to log value to the base 10.
data EMP_DET1; set EMP_DET; LOG10_salary = LOG10(salary_in_USD); run;
So the resultant table with logarithmic base 10 value will be