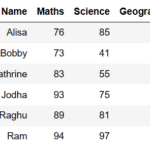
We can Join or merge two data frames in pandas python by using the merge() function. The different arguments to merge() allow you to perform natural join, left join, right join, and full outer join in pandas. We have also seen other type join or concatenate operations like join based on index,Row index and column index.
Join or Merge in Pandas – Syntax:
left_df – Dataframe1
right_df– Dataframe2.
on− Columns (names) to join on. Must be found in both the left and right DataFrame objects.
how – type of join needs to be performed – ‘left’, ‘right’, ‘outer’, ‘inner’, Default is inner join
The data frames must have same column names on which the merging happens. Merge() Function in pandas is similar to database join operation in SQL.
UNDERSTANDING THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF JOIN OR MERGE IN PANDAS:
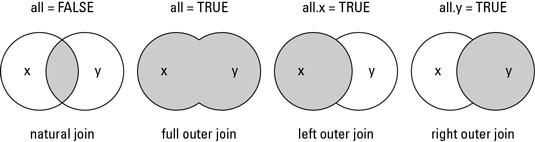
- Inner Join or Natural join: To keep only rows that match from the data frames, specify the argument how=‘inner’.
- Outer Join or Full outer join:To keep all rows from both data frames, specify how=‘outer’.
- Left Join or Left outer join:To include all the rows of your data frame x and only those from y that match, specify how=‘left’.
- Right Join or Right outer join:To include all the rows of your data frame y and only those from x that match, specify how=‘right’.
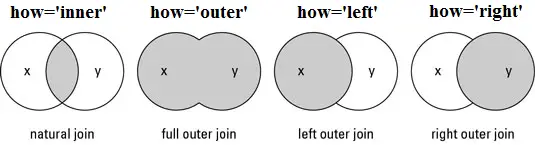
Lets try different Merge or join operation with an example:
Create dataframe:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# data frame 1
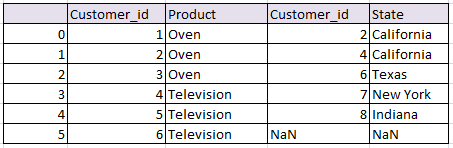
d1 = {'Customer_id':pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6]),
'Product':pd.Series(['Oven','Oven','Oven','Television','Television','Television'])}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(d1)
# data frame 2
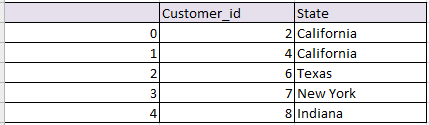
d2 = {'Customer_id':pd.Series([2,4,6,7,8]),
'State':pd.Series(['California','California','Texas','New York','Indiana'])}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(d2)
so we will get following two data frames
df1:
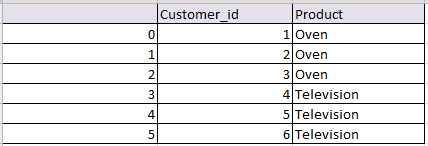
df2:
Inner join pandas:
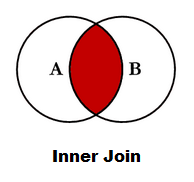
Return only the rows in which the left table have matching keys in the right table
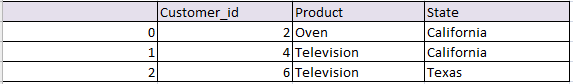
#inner join in python pandas inner_join_df= pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Customer_id', how='inner') inner_join_df
the resultant data frame df will be
Outer join in pandas:
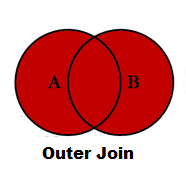
Returns all rows from both tables, join records from the left which have matching keys in the right table.When there is no Matching from any table NaN will be returned
# outer join in python pandas outer_join_df=pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Customer_id', how='outer') outer_join_df
the resultant data frame df will be
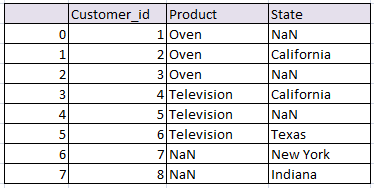
Left outer Join or Left join pandas:
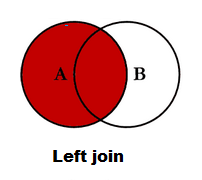
Return all rows from the left table, and any rows with matching keys from the right table.When there is no Matching from right table NaN will be returned
# left join in python left_join_df= pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Customer_id', how='left') left_join_df
the resultant data frame df will be
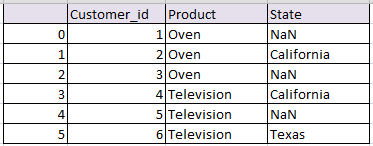
Right outer join or Right Join pandas:
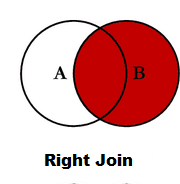
Return all rows from the right table, and any rows with matching keys from the left table.
# right join in python pandas right_join_df= pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Customer_id', how='right') right_join_df
the resultant data frame df will be
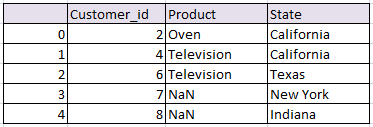
OTHER TYPES OF JOINS & CONCATENATION IN PANDAS PYTHON
Join based on Index in pandas python (Row index):
Simply concatenated both the tables based on their index.
# join based on index python pandas df_index = pd.merge(df1, df2, right_index=True, left_index=True) df_index
the resultant data frame will be
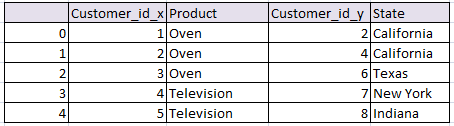
Concatenate or join on Index in pandas python and keep the same index:
Concatenates two tables and keeps the old index .
# Concatenate and keep the old index python pandas df_row = pd.concat([df1, df2]) df_row
the resultant data frame will be
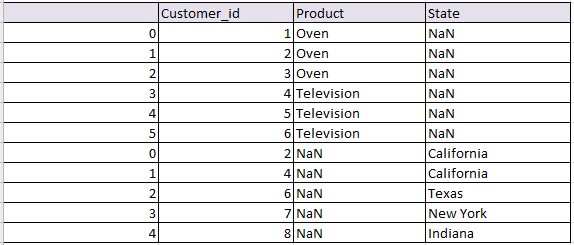
Concatenate or join on Index in pandas python and change the index:
Concatenates two tables and change the index by reindexing.
# Concatenate and change the index python pandas df_row_reindex = pd.concat([df1, df2], ignore_index=True) df_row_reindex
the resultant data frame will be
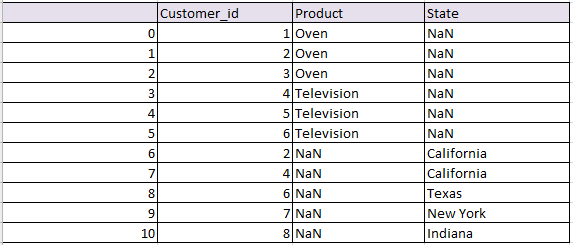
Concatenate or join based on column index in pandas python:
Simply concatenated both the tables based on their column index. Axis =1 indicates concatenation has to be done based on column index
# join based on index python pandas df_col = pd.concat([df1,df2], axis=1) df_col
the resultant data frame will be