Natural Log and Log transformation of the column in R is calculated using log10() and log() function. Let’s see how to calculate
- Natural Log of the column in R with example
- Log transformation of the column in R with example
Let’s first create the dataframe
df1 = data.frame(Name = c('George','Andrea', 'Micheal','Maggie','Ravi','Xien','Jalpa'),
Mathematics_score=c(45,78,44,89,66,49,72),
Science_score=c(56,52,45,88,33,90,47))
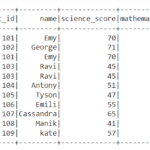
df1
So the resultant dataframe will be

Natural Log of the column in R:
Natural Log transformation of the column in R is calculated using log() function as shown below.
df1[,c(2,3)] <- log(df1[,c(2,3)]) df1
so the resultant natural log transformed data will be

Log of the column in R:
Log transformation of the column in R is calculated using log10() function as shown below.
df1[,c(2,3)] <- log10(df1[,c(2,3)]) df1
so the resultant log transformed data will be